Prologue: A Journey Through the Tapestry of Artistic Endeavors
Art, a universal language transcending boundaries, has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations, documented historical events, and reflected human aspirations throughout the ages. This comprehensive article delves into a panoramic exploration of world art history, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern marvels.
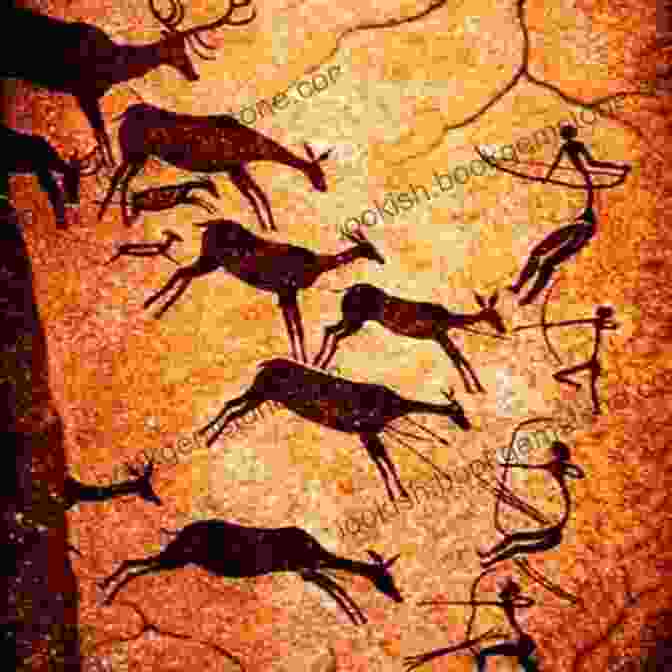
Chapter I: The Dawn of Creativity - Stone Age Artistic Expressions
The earliest artistic endeavors emerged during the Stone Age, where cave paintings and sculptures depicted scenes of hunting, ceremonies, and animals. These works, often found in remote caves and rock shelters, provide insights into the spiritual beliefs, daily lives, and artistic skills of prehistoric societies.
4.1 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 264971 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 978 pages |

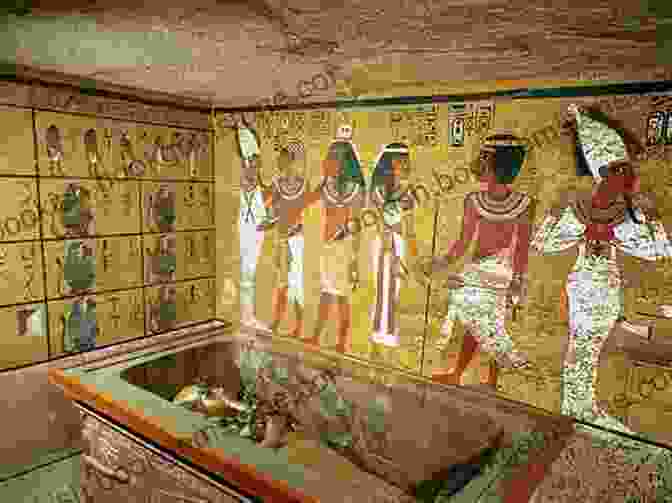
Chapter II: Ancient Civilizations and Artistic Flourishing
As civilizations arose in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, and Rome, art played a central role in religious rituals, political propaganda, and aesthetic expression. Mesopotamian temples featured elaborate reliefs, while Egyptian tombs contained exquisite paintings and sculptures portraying scenes from the afterlife. Greek art, known for its idealized forms and harmonious balance, influenced artistic styles for centuries to come.

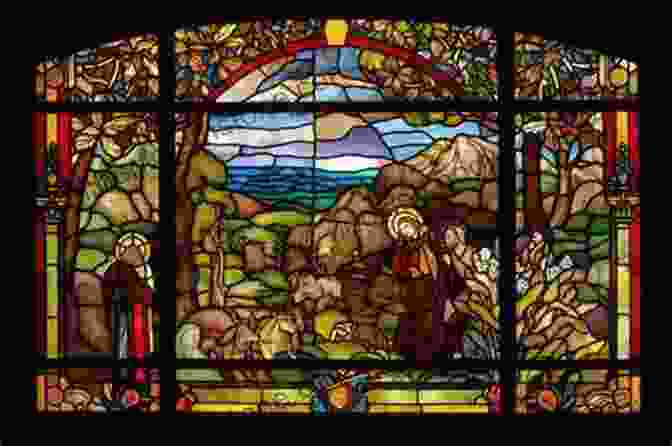
Chapter III: The Middle Ages and the Rise of Christianity
The Middle Ages witnessed a shift towards religious art, with churches and cathedrals adorned with impressive stained glass windows, mosaics, and sculptures. Byzantine art, with its iconic mosaics and frescoes, portrayed divine scenes and biblical narratives. Romanesque and Gothic architecture showcased towering spires, intricate carvings, and elaborate stained glass, reflecting the religious fervor and technical prowess of the era.

Chapter IV: The Renaissance and the Birth of Humanism
The Renaissance marked a profound revival of classical art and architecture. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael embraced humanism, portraying subjects with realistic proportions and expressions. The invention of oil paints allowed for richer colors and sophisticated techniques, leading to masterpieces that continue to inspire awe.
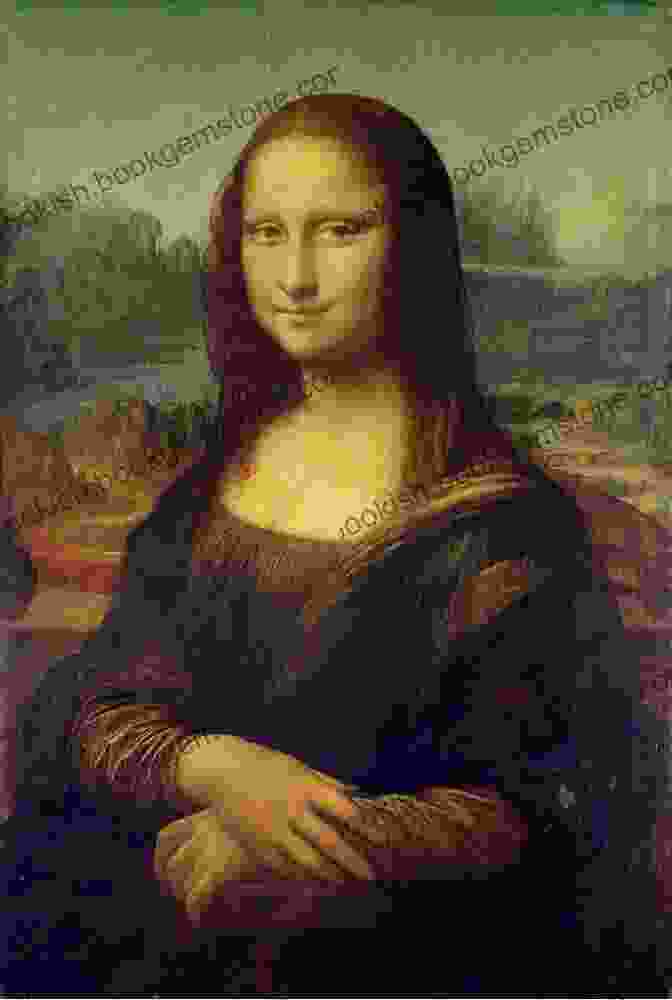

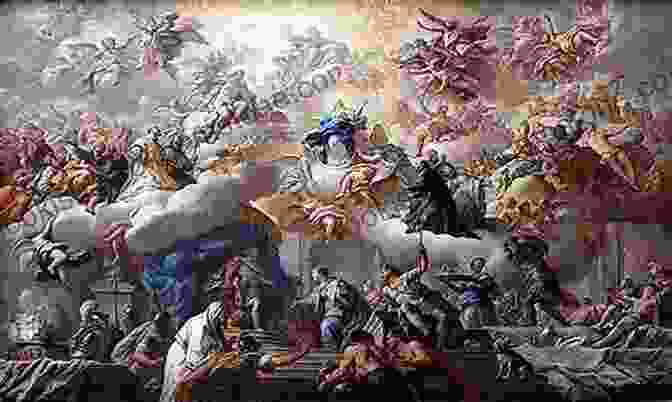
Chapter V: The Baroque Era and Artistic Extravagance
The Baroque period saw a surge in opulence and grandeur in art. Paintings and sculptures depicted dramatic scenes with vibrant colors, dynamic compositions, and elaborate embellishments. Architects designed elaborate palaces and churches with soaring domes, intricate facades, and sweeping staircases. The Baroque style dominated until the rise of Neoclassicism in the 18th century.

Chapter VI: Romanticism and Nature's Embrace
Romanticism emerged as a reaction to the formality of Neoclassicism. Artists sought inspiration from nature, expressing their emotions and subjective experiences through dramatic landscapes, allegorical paintings, and Gothic novels. The movement influenced music, literature, and art for decades, capturing the imagination of a generation.

Chapter VII: Impressionism and the Play of Light
Impressionism, a groundbreaking movement of the late 19th century, emphasized the capturing of fleeting moments and the play of light. Artists like Monet, Renoir, and Degas painted en plein air, capturing the changing colors and textures of the natural world. Impressionism revolutionized painting techniques and laid the foundation for modern art.

Chapter VIII: Modernism and the Search for Abstraction
Modern art emerged in the early 20th century and challenged traditional artistic norms. Artists like Picasso, Kandinsky, and Klee embraced abstraction, experimenting with non-representational forms, bold colors, and unusual materials. Modernism encompassed various movements such as Cubism, Futurism, and Abstract Expressionism.
Chapter IX: Post-Modernism and Beyond
The post-modern era witnessed a return to representational art and a questioning of the traditional definitions of what constitutes art. Artists incorporated elements of popular culture, mass media, and everyday objects into their works. Contemporary art continues to evolve, embracing a wide range of styles and mediums, reflecting the complexities and diversity of our modern world.

Epilogue: The Enduring Legacy of Artistic Creation
Throughout history, art has played a vital role in documenting human experience, expressing cultural values, and inspiring future generations. The Fully Illustrated Panoramic World History of Art offers an immersive journey into the grandeur of artistic achievements, showcasing the endless creativity and ingenuity that have defined humanity throughout the ages.